On the modeling of fiber dispersion in fiber-reinforced elastic materials
Andrey V. Melnik, Hudson Borja Da Rocha, and Alain Goriely
International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, Mar 2015
Instabilities and Nonlinearities in Soft Systems: From Fluids to Biomaterials
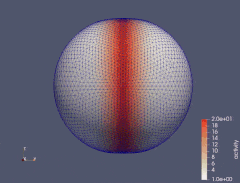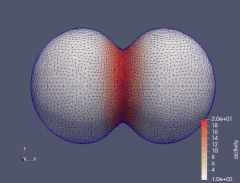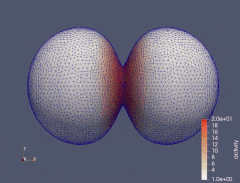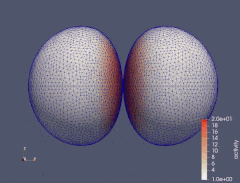
When an isotropic material is subject to a uniaxial tension, the principal strain transverse to the direction of applied load is always negative. However, in fiber reinforced materials the transverse principal strain can change its sign as the load increases, passing through the zero-points, known as perversions. We investigate how the number of perversions in a material reinforced by two symmetrically aligned families of distributed fibers depends both on the degree of fiber dispersion and the model used for fiber dispersion. Angular integration and three variants of the generalized structure tensor approach are considered and discussed. The study of perversions clearly demonstrates the qualitative difference between these approaches in the case of high dispersion of fibers. The results suggest that this difference is primarily due to the way compressive fibers are modeled.
 A plausible mechanism of muscle stabilization in stall conditionsThe European Physical Journal Plus, 2021
A plausible mechanism of muscle stabilization in stall conditionsThe European Physical Journal Plus, 2021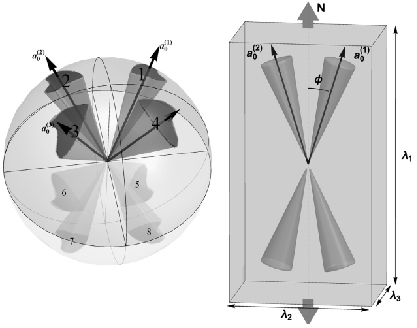 On the modeling of fiber dispersion in fiber-reinforced elastic materialsInternational Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, Mar 2015Instabilities and Nonlinearities in Soft Systems: From Fluids to Biomaterials
On the modeling of fiber dispersion in fiber-reinforced elastic materialsInternational Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, Mar 2015Instabilities and Nonlinearities in Soft Systems: From Fluids to Biomaterials